This a Small Comet post. For those of you who are unfamiliar with Louis A Frank’s discovery of Small Comets forty years ago, here's a brief overview. Regular readers of Abbott's Almanac know this is the ground I plow, so for your sake it will be brief. Frank was a brilliant professor and experimental physicist at the University of Iowa. He was NASA'S principal investigator for the imaging equipment on the Dynamics Explorer Spacecraft I & II. Frank designed the cameras and the imaging equipment on board. He and his team built them. No man works alone. But Frank was definitely the boss. The Dynamics Explorer team was imaging the Aurora Borealis and Earth's ultraviolet day glow. “Spots” in the very first images in early 1982 were crashing the program his graduate students had written to process the images. Frank, being obsessive about his equipment, didn't want to work around the spots, he wanted to find out what was causing the spots. They quickly found the spots were not instrument noise. The team confirmed the equipment was capturing physical events that were obscuring the UV dayglow they were recording with their photographic instruments. They had discovered what they called ‘atmospheric holes.’ The Small Comet name came later after they concluded the obscuring agent of the dayglow had to be a dense cloud of water vapor. It took a couple of years to exhaust all the other possible causes.
The Small Comets were a hitherto undiscovered class of planetary objects and had an annual infall into Earth's atmosphere that they calculated to be around ten million a year. Frank correctly objected to applying the terms, meteor and meteoric, to the Small Comets. Not only were these new objects numerous, but they were on average, big compared to meteors. Frank estimated the Small Comets were the size of a small house and in the mean weighed forty tons. The very visible stony-iron meteors we see in the night sky typically weigh between a few grams to several kilograms. Unlike meteors, nobody can see the Small Comets themselves. Frank's team could only see the Small Comets’ debris fields. The little spots on the images were large, (twenty to thirty miles across) plummeting veils of dense water vapor. It would have been easy to find a programming workaround for the spots in the images. Frank’s dedication to the principles of discovery and truth makes him a true outlier among scientists. Who could have known those black specks represented the most important discovery since Kepler’s discovery of the planets’ elliptical orbits? That discovery confirmed Copernicus’ heliocentric solar system. The reason Frank chose the term, ‘small comets’ forty years ago is because comets were about the only known water bearing planetary objects known in the solar system. Comets are not meteors. Frank’s Small Comets are properly called cometary-like objects, at least according to Frank.
Frank hypothesized the physical structure of the Small Comets must be like a snowball encapsulated in a thin carbon mantle. The carbon would make the Small Comets difficult to see and protect the water-ice snowball from sublimating in space and sunlight. I don't think Frank thought the carbon mantles could be particularly durable or strong because the evolutionary thinking about the Universe's origins requires the formation of the planetary and stellar objects to be dependent on their gravity to sort, order and layer the planetesimals (the parts, the dust) into the whole. Frank always assumed the increasing heat from the sun would destroy the Small Comets once they were pulled closer to the Sun, probably just inside Earth's orbital path.
After the Small Comet discovery, Frank basically spent the balance of his career trying to get his peers to acknowledge his data. No one has ever shown Frank's data to be in error. The few scientists who seriously tried to replicate his findings successfully did so. The real problem was his peers could not believe so many large, heavy, and to their minds, ‘meteoric’ objects could be falling into Earth's atmosphere every minute of every day and never be seen. His peers knew how to look at the sky too. Most were never going to see them. They didn’t expect to see them either. That was a big part of the problem. There was a whole lot of confirmation bias going on. They didn’t believe Frank because his discovery was so extraordinary. “Seeing is believing” is an old saw. But we choose what we believe. Frank’s colleagues and peers wanted to believe they were seeing instrument noise when they looked at Frank’s images, so they ignored and/or misrepresented his data and got the answers they believed in.
Frank's discovery is now essentially forgotten. But the debris field evidence for the Small Comets continues to accumulate, and not just on earth. This article is, in some ways, a Part II to the Abbott’s Almanac piece published this past January, Dark Matter Day. I believe Frank’s Small Comets are indeed the dark matter that makes up perhaps eighty-five percent of the Universe’s mass. This current article will more or less confine itself to the evidence that the Small Comets are infalling into every star in the Universe at rates which are orders of magnitude greater than Earth's infall.
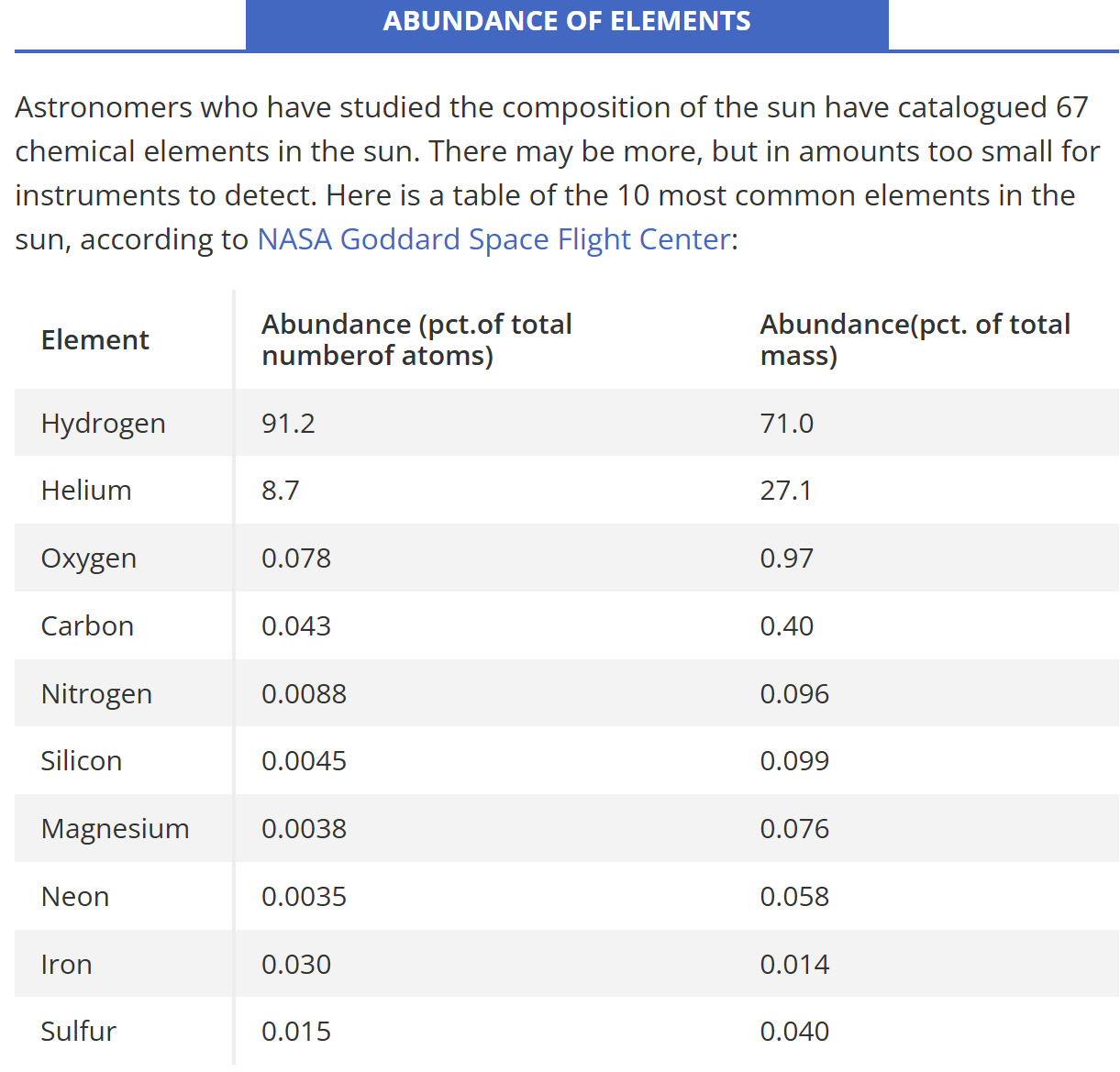
There are many different types of stars, but essentially, they are all about ninety percent hydrogen and ten percent helium in atomic ratio. Less than two percent of a star is composed of elements other than hydrogen and helium. And here is the kicker: oxygen and carbon account for most of that remaining two percent.
The chart above is for our Sun, but it will more or less work for every star. There will be so-called ‘iron-rich’ or ‘carbon-rich’ stars, but the table’s values won’t change much. The red, cooler, carbon-rich stars might even have an inverse carbon/oxygen ratio. But carbon and oxygen are always either number three or number four in the table. Water is visible in the spectra of cooler stars too. Water has been imaged in our Sun’s cooler, sunspots since at least 1919. We can’t ‘look’ inside the stars. We can only see their surfaces, that is, their stellar atmospheres. Universally it is assumed the stars are making all these visible minor elements in the interior and core through nucleosynthesis, which more or less means fusion. The stars are assumed to be ‘making’ water in their atmospheres/surfaces too, but these are wrong assumptions, and therefore flawed hypotheses.
The stars are unmaking the small comets. Water molecules don’t begin to atomically disassociate into hydrogen and oxygen atoms until they reach 2000 K. But they only start to come apart pretty thoroughly when you get above 4500 K. The Red Stars temperatures are around 3000 K, about the temperature where half the water molecules will be disassociated. It would be entirely appropriate to call Red Stars, water-rich stars. One of the mysteries about how our Sun and the stars could be making water is there isn’t enough visible oxygen for the task. Rather, the oxygen that is visible comes from the disassociated water molecules delivered constantly by Frank’s Small Comets.
The simple hypothesis: The oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and all the other trace elements that are spectrally visible on the surfaces of stars are being delivered by Frank’s Small Comets, his Cosmic Rain. Those visible stellar elements and the water are not being conjured from the depths of the stars by nucleosynthesis. It’s an understatement to say stellar nucleosynthesis is not well understood. It’s complicated conjecture and rank speculation. A massive, ongoing, infall of Frank’s Small Comets is a very simple, coherent, observation-based hypothesis.
Frank was wrong in some of his assumptions about the dusty, particulated, Small Comet carbon mantles. If the Small Comets are intact all the way to our Sun and indeed to all the stars, then the carbon mantles must be exotic, thin and extremely strong and heat resistant. There was no flaw in Frank’s reasoning - his understanding of the carbon mantle formation process made it more or less a ‘fragile mantle.’ Frank based his understanding on the principle the Small Comets pulled their parts out of the ever-expanding hydrogen-derived remnants of the Big Bang.
But the creative words, “let there be light” is not the beginning of the creation story.
In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth. And the earth was without form, and void; and darkness was upon the face of the deep. And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters. And God said, let there be light: and there was light.
Frank imagined the Small Comets were formed somewhere in close vicinity of our solar system. But I surmise the Small Comets emerged from the crucible of origins at that particular time when God said, ‘let there be light’ and He separated the light from the darkness and separated the waters above the heavens from the waters below the heavens. In the creation story, water precedes light. There was a lot of darkness and water present at the Big Bang - all before there was light.
"It's another demonstration that water is pervasive throughout the universe, even at the very earliest times." Matt Bradford, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory - Speaking about a Quasar with an estimated one hundred and forty trillion Earth-oceans of water. Frank and his peers had a thimble full of knowledge about how much water is in the Universe forty years ago. We now have oceans of knowledge. We are just now coming of age and realizing the Universe, like the human body, is mostly water.
Frank’s Small Comets are everywhere in the Universe, and they are as old as the creation event itself. They are Dark Matter, (dark matter was another thing that was not yet much of a thing in Frank’s day.) Their carbon mantles are beyond exotic, they are incredibly strong and hard and perfectly stealthy.
Toward the end of his career Frank had begun to connect the Small Comet carbon mantles with the emerging stealth technology being developed for military aircraft. He proffered that as one of the explanations as to why the Naval Research Lab radar which Steven Knowles used to search for the Small Comets could not see them. When I found out nitrogen was the fifth most common element in the spectral analysis of starlight, I started to google terms like ‘carbon nitrides’ and ‘stealthy’. This is a subject of intense military work and interest. Exotic carbon structures like graphene and carbon nanotubes form only under immense pressure, similar to diamonds. Below is just the smallest sample of what they are discovering. It’s no more than a clipped abstract and I place it in the article here to give the reader a taste of how crazy and exotic things can be with carbon under pressure. Diamonds in the rough, indeed. Invisibility Paint.
Conclusion
The oxygen in the atmospheres of all stars. It comes from the disassociated water molecules which are constantly being delivered by the Small Comets. The water observed on all red stars comes from the Small Comets. The carbon and nitrogen and other trace elements observed in all the stellar atmospheres in the universe is also from the Small Comets. This conclusion is reasonable and is drawn from observations, not speculation. The complex and widely variable stellar pressures and temperature intensities make nucleosynthetic fabrication of the visible elements quite unlikely, a flawed hypothesis to the core. The almost monotonously similar spectral analysis of the elements in the atmospheres of our Sun and the stars make Small Comets the likely source of the water and elements observed in the light spectra of stellar atmospheres.
Frank’s adversarial peers, who were terribly disrespectful of Frank’s data and his integrity, think they won the debate and there are no Small Comets. Guess what? There is a wall of water building behind a dam of circumstantial Small Comet evidence that, when it breaks, will utterly ruin the reputations of the scientists who wouldn’t truthfully engage Frank’s team’s experiments, data, or the spirit of discovery. The history of science will always remember them, but as antagonists of the experimental method and the antithesis of collegial inquiry.